Triggers: API Route
For managing API routes, one of the most common trigger for invoking data processes. If multiple data processes are linked to an API route, they will be invoked synchronously.
See Create and Use an API Route Trigger for how to create an API route in Studio.
Create an API Route
After creating a project in the Data Process panel or upload one via CLI, you can right-click the project in the API Route panel and click Create API Route.
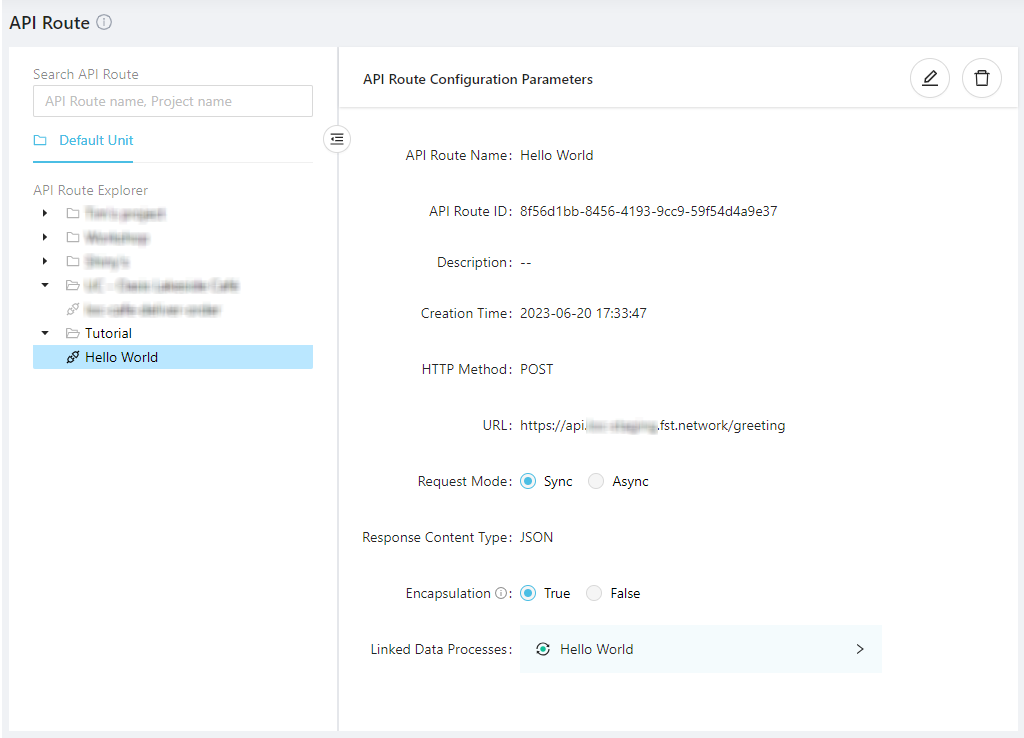
An API route has the following options:
- HTTP method
- API path and prefix
- Request mode (synchronous or asynchronous)
- Response content type (auto, JSON, YAML or XML)
- Encapsulation (whether or not to encapsulate task results in execution metadata; default
true) - Linked data processes
A new created or modified API route would require a little time - several to a dozen seconds - to deploy or take effect (the gateway may return code 404 before the route is ready).
An API route returns one of the following HTTP code:
200indicates the (synchronous) API route has received an execution result within timeout (15 seconds).202indicates the API route has triggered an execution but have not received the result (either the API is asynchronous or the execution did not finish due to some reason).
A synchronous API route may still return 202 if the data process(es) take more than 15 seconds to run, while still generate correct results in execution history.
If you wish to return task result(s) only without the execution metadata (which means you can fully customise the API result), set the encapsulation to false, although you will not be able to retrace metadata like execution or task IDs.
If a data process has been linked to an API route, and you later create a new revision of the data process, you'll have to manually re-link it to the API route (modify the API route then link again).
If a linked data process contains missing agent configurations, it won't be able to be executed.
Be noted that LOC gateway does not recognize additional path appended after an deployed API route. For example, when invoking an API route /api/v1/my-service, /api/v1/my-service/{id} would return 404. You can use QueryString instead, for example, /api/v1/my-service?id={id}.